It has been said that one man cannot change history. Alexander the Great, Christopher Columbus, Napoleon Bonaparte, and Abraham Lincoln, all brought out the best and the worst in men. Throughout time, we have put immense power in the hands of few and now their names live on forever. But how can one man change history? How does the son of an Austrian factory worker come to European power and become responsible for the deaths of as many as 35 million people?
Adolph Hitler was born in the year 1889. His father died in 1912 and left him a meager inheritance. Adolph fancied himself a sensitive artist, and moved from Austria to Bavaria where many unemployed artists of his time lived. Bavaria was much like Greenwich Village in the 1960's and Adolph Hitler was a hippie of sorts. World War I was in full swing, at the time, and Austria sent Hitler his draft notice, which he claimed he never received. He was arrested for dodging the draft and was sent back to Austria. Upon his return, he was sent to take his Army physical and flunked. He returned to Bavaria and there enlisted in the German Army as an Austrian citizen. After basic training, Hitler was sent to the Western Front where he was assigned the duty of messenger. He was responsible for running orders from the Field Commander to the front line, usually under heavy fire. Hitler was twice awarded the Iron Cross. He beat incredible odds just to survive and later referred to his days at the Front as the best of his life. In October, 1918, he was blinded by poisionous gas and was still recovering when the Armistice cease-fire was signed.
After the Treaty of Versailles was signed, ending World War I, Corporal Hitler went to work for the Weimar (democratic) government, as a spy. His job was to observe the new political parties starting up in Germany and his orders were to watch and attend the meetings of the German Workers party in Munich. Hitler reported that the group was not very threatening, that they mostly got together, drank beer, got drunk, and went home. Regardless, Hitler was ordered to infiltrate the organization and become a member. He was quickly accepted into the group and was put in charge of recruitment and propaganda. In Februaury of 1920, Adolph Hitler gave his first recruitment speech, one which would become familiar. He spoke about anti-semitism, anti Treaty of Versailles, anti democracy. One week after this meeting, the party changed its name to the National Socialist German Workers Party -- NAZI.
Up to this point in his life, Hitler had been an introvert with no friends; he was painfully shy and afraid of large crowds. All of this was changing, and in April of 1920 he resigned from the German Army. He now would devote all his energy to politics and the Nazi party. Hitler, at the age of thirty-one, had finally found something he was good at. Did he fall into this by sheer luck? Or was it destiny? This was a man whose high school guidance counselor likely told him he would never amount to anything. Hitler did research on German mythology and adopted the Swastika as the symbol of the party because, according to myth, it is the symbol of the beginning of all creation. Hitler was beginning to create his ideal world.
In 1923, Hitler thought it was time to make his move; he organized a putsch (a take-over of a government) on the city of Munich. It failed miserably. Hitler and his followers were arrested and charged with treason. Hitler turned his trial into a propaganda triumph and received a great deal of publicity when he pleaded guilty, not of treason, but of being a patriot. He was sentenced to five years in prison, but he never served his full time because no one in authority truly believed him to be any kind of a threat.
Hitler learned many lessons from the failed Munich putsch; prison gave him time to think and set goals. While imprisoned, he wrote a book entitled Mein Kampf, meaning, my struggle. In his book he explains his ideas on race, and describes his ideas for his Two Thousand Year Government moving into the east and taking over Russia. It completley explained all of his plans, which he would eventually follow to the ‘T'. Hitler believed that he had survived World War I because it was his destiny to create the third German empire -- the Third Reich. It was all there in black and white and no one bothered to read the book except Winston Churchill, who was denounced for expressing concern about Hitler when the rest of the free world was preoccupied with fears about Russia and communism.
Once out of jail, Hitler started to rebuild his party and was secretly receiving subsidies from the German army in support of the Nazi party. He started using powerful propaganda that would eventually become known as The Big Lie. The theory behind the Big Lie was that the masses would believe a big lie more than they would belive a little lie, if they heard it often enough. Hitler bombarded the people with talk of peace, nonviolence and a strong unified Germany, while all along he was sytematically planning to attack Russia and purge Germany of all non-Arians. Hitler made his Nazi party as visable as possible, using bright colored uniforms, arm bands, flags and banners. He glorified the military by starting the Hitler Youth program. Hitler established his S.S. (the secret police) to act as his body guards and started out with seventy five soldiers. Hitler placed Heinrich Himmler at the head of the S.S., an evil, wicked man who would eventually be responsible for the murders of millions of people. Himmler himself only ever witnessed one execution, as his stomach was too weak for the gore. He lost his lunch.
The Weimar government was run by a coalition of fascists, communists, socialists, and so on. All of the parties were pulling for power and when they had to elect a new Chancellor of Germany, none of the parties had enough votes to win the position, so they all decided to elect Hitler, as a puppet figurehead, because he seemed harmless enough. In 1933, Hitler was elected by a democratic process to the position of Chancellor of Germany. Less than one month after he was elected Chancellor, a fire broke out in the Reichstag building (similar to our congress) known as the Reichstag Fire. Hitler seized the moment and claimed the fire was really a coup attempt by the communists. The S.S. destroyed documents and framed the communists. All of the communist leaders were arrested and sent to Dachau -- the beginning of the concentration camps. As Chancellor of Germany, Hitler declared a state of emergency, taking away all personal rights and freedoms. The accidental fire allowed Hitler the opportunity to become Dictator.
In April, 1933, Hitler issued another decree, blaming the Jewish people for all of Germany's problems. A boycott of all Jewish business took place over a period of months. Hitler segregated the Jews. The German people did not buy into beliefs of antisemitism and Hitler knew that even a dictator needed the support of the people to go to war; so, under the cloak of darkness and secrecy, Jews began to disappear from their homes.
On June 30, 1934, Hitler ordered his S.S. to begin killing Nazi party leaders. They were ordered to kill anyone too weak or too strong. This was known as the Night of Long Knives. He required absolute, blind loyalty or you died. Hitler successfully purged his party of all his rivals. He now had one party, that of Adoph Hitler.
As the saying goes, the rest is history. One man did change the world forever. Was Hitler's rise to power truly destiny? The hippie son of an Austrian factory worker leading the most feared Nazi government. Few men have had such an impact as Adolph Hitler. He did bring out the best and worst in men and his name lives on forever. After Hitler's reign of power the world became a different place than it had been before and it will never be the same again.
Sunday, March 28, 2010
SHAHJAHAN

¤ Shah Jahan-The Favorite Grandson of Emperor Akbar
The scene of history shifts to Delhi again with Shah Jahan (of the Taj Mahal fame), the son of Jahangir ascending the throne. Shah Jahan was the grand old emperor Akbar’s favorite grandson. In fact, at one time there was a genuine fear that the sovereign would name him, instead of his son, as the successor. This was largely because Akbar regarded Jahangir as a bit of a bounder who whiled away his time with wine and women from a startlingly young age. One of the most famous movies in Indian cinematic history is Mughal-e-Azam (a must-see) which, if you take away the romantic trimmings, is all about Akbar saving Jahangir from his romantic excesses.
¤ Shah Jahan's Strain Relations With His Father Jahangir
Jahangir got a taste of his own medicine when he was king and his son Shah Jahan (then Prince Khurram) revolted against him. Jahangir had to eventually resort to the extreme measure of kidnapping his own grandchildren away to Kashmir with him to shut his son up. What drove Shah Jahan further away from his father was the intense court intrigue with the calculating Nur Jahan at the hub. Jahangir, while being every inch an autocrat, was completely dependent on his extremely capable and shrewd wife, Nur Jahan. The queen had a daughter from a previous marriage, and she wanted to see her daughter’s husband safely to the throne. Nur Jahan, who could not have expected to win any popularity contests in Agra, went alone in this choice. A major chunk of the nobility was with Shah Jahan. However it was she who had, as they say, the king’s ear. So despite the fact that Jahangir agreed to forgive and forget Shah Jahan’s misadventures in 1625, the tension could not be defused entirely.
¤ Shah Jhan Chosen As A Successor of The Throne
When Jahangir died in 1627 in Lahore, the Queen tried all the tricks in the book to put her candidate on the throne. But it was all in vain. Shah Jahan ascended the throne on popular demand, Nur Jahan retired from public life and her son-in-law was imprisoned.
¤ The Golden Period of The Mughal Dynasty.
The reign of Shah Jahan has been widely acclaimed as the golden period of the Mughal dynasty. There are many reasons for this. Thanks to the firm base left by his grandfather and father, Shah Jahan’s reign was relatively peaceful and hence prosperous. Except for a drought in 1630, in the areas of Deccan, Gujarat and Khandesh, the kingdom was secure and free from poverty. The coffers of the state were brimming with the right stuff. So it’s no wonder that Shah Jahan was the greatest and most assiduous builder of the Mughal dynasty.
¤ Shah Jhan- Undoubtedly A Great King
In 1639, he decided to shift his capital to Delhi and construct a new city on the banks of the Yamuna, near Ferozabad. It was to be called Shahjahanabad. Work on the fort and city commenced in 1639 and it took 10 years to build the Red Fort and palace. The spectacular peacock throne (the one that Nadir Shah took away) was transferred from Agra to the Red Fort, the new seat of the Mughal rulers, on April 8, 1648.
Jahangir had built a great reputation for himself as a dispenser of justice and Shah Jahan carried forward the good work and took a personal interest in the judiciary. He demanded a high standard of law and order and even petty thieves were not spared. The age was pretty dynamic in the sense that there was intense interaction with foreign countries and travellers poured into India from Persia, France, Italy, Portugal and England. Which is very interesting for the scholar, for one gets accounts of people from myriad nationalities during the Shah Jahan’s reign.
Shah Jahan was undoubtedly a great king. He had shown evidence of being a great general even under his father’s reign. Military genius apart, his capacity for hard work is also legendary. A good administrator, he saw to it that the government machinery moved on oiled wheels. Within a year of his becoming king, the revenue of the state had shot up meteorically.
¤ The Breathtaking Constructions of Taj Mahal
Shah Jahan was an aesthete and loved building. His greatest achievements of course were the breathtaking Taj Mahal, which he built in the memory of his wife Mumtaz Mahal, and the magnificent city of Shahjahanabad, which remained the capital of India till well into the 19th century.
There was a downside, of course. He was a bigoted Muslim and a confirmed nepotist. He provided for the imperial princes before anyone else in the matter of administrative and judicial postings regardless of age, capability and talent. He also started the practise of bestowing each prince with an important office. For instance, Dara Shikoh was made the governor of Punjab and Multan while Aurangzeb was appointed governor of all the four provinces of the Deccan. This might have just been a clever way to keep them occupied but that was not how the nobility saw it. The nobles viewed the practice as an obstacle in the path of their prosperity and promotions.
¤ Emperor's Devin Love For His Wife Mumtaz Mahal
It is said that Shah Jahan died in spirit the day his Queen Mumtaz died. Stories are told of how he shut himself up in a room after her death and when he came out next morning his hair had turned white. A nice romantic tale, but the truth is that for all his love, Shah Jahan did not hesitate to expose Mumtaz to the rigours of travel in all states of health so that she died at the young age of 39 after giving birth to their fourteenth child. Also he was quick to seek consolation elsewhere and married several other women after Mumtaz died. However the love for Mumtaz must have been enduring, for when he was old and dying he began missing his queen all over again. By that time however, the power equation had changed once again.
¤ The Peacock Throne
The fantastic Peacock Throne of the Mughals is now only a blurred memory in the collective imagination of Indians. It is now only alluded to illustrate the splendour and riches of India and all our lost glory. Painstakingly created by skilled craftsmen and artisans between 1628 and 1635, it was carried away to Persia by the marauding Nadir Shah in 1739. There are however still some miniature paintings that depict Akbar and Jahangir sitting proud on it. Shaped as a golden bedstead with golden legs and an enamelled canopy supported by 12 pillars, it looks breathtakingly fabulous. Each of the 12 emerald pillars bore two peacocks encrusted with gems and a tree with diamonds, emeralds, rubies and pearls nestled between each pair of birds. Just look at the picture - can you guess how much it cost?
A whopping 10 million rupees, equivalent then to a million and quarter pound sterling.
INDIAN SATELLITES
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
Oceansat-2 23 September 2009
IMS-1 28 April 2008
Cartosat-2A 28 April 2008
CARTOSAT-2 10 January 2007
IRS P5 (CARTOSAT-1) 5 May 2005
IRS P6 (Resourcesat 1) 17 October 2003
IRS P4 (Oceansat 1) 27 May 1999
IRS P3 21 March 1996
IRS P2 15 October 1994
IRS P1 (also IE)(Crashed, due to launch failure of Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle, 20 September 1993)
IRS 1D 29 September 1997
IRS 1C 28 December 1995
IRS 1B 29 August 1991
IRS 1A 17 March 1988
Oceansat-2 23 September 2009
IMS-1 28 April 2008
Cartosat-2A 28 April 2008
CARTOSAT-2 10 January 2007
IRS P5 (CARTOSAT-1) 5 May 2005
IRS P6 (Resourcesat 1) 17 October 2003
IRS P4 (Oceansat 1) 27 May 1999
IRS P3 21 March 1996
IRS P2 15 October 1994
IRS P1 (also IE)(Crashed, due to launch failure of Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle, 20 September 1993)
IRS 1D 29 September 1997
IRS 1C 28 December 1995
IRS 1B 29 August 1991
IRS 1A 17 March 1988
JAVA TIPS


1. Flush Streams
This might seem obvious, but it repeatedly kicks my butt. The problem usually appears with two programs on either side of a network socket having some kind of conversation. If you don't flush the output stream every time you say something, the data may not actually get written out to the socket, and the two programs will sit patiently, waiting forever for something to happen.
Typically, you can just call flush() after you write something important:
// OutputStream out;
// byte[] data
out.write(data);
out.flush();
If you're writing text data, you might use a PrintWriter for output. PrintWriter has a special constructor that lets you specify if the stream should be flushed after every newline:
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(rawOut, true);
A PrintWriter created in this way will automatically flush itself whenever you write a line of text.
2. Use Antialiasing
This is a sweet one. If you're doing any graphics at all in Java 2, you can make it look a lot nicer with a single line of code. Consider the following paint() method:
public void paint(Graphics g) {
g.setColor(Color.green);
g.drawLine(20, 20, 40, 140);
g.setColor(Color.blue);
g.fillOval(50, 110, 120, 60);
g.setColor(Color.red);
g.setFont(new Font("Serif", Font.ITALIC, 36));
g.drawString("Cellini", 40, 80);
}
I haven't even used any 2D API features here--it's just plain old AWT graphics stuff. Adding antialiasing is easy. Just add this line to the very top of the paint() method:
((Graphics2D)g).setRenderingHint
(RenderingHints.KEY_ANTIALIASING,
RenderingHints.VALUE_ANTIALIAS_ON);
The difference is shown below. It's great stuff for free!
Aliased rendering (default)
Antialiased rendering
3. Subclass JComponent, not JPanel
If you're creating a new graphical component, subclass JComponent. It's the base class for all Swing components. JPanel, as a container, has some extra baggage for double buffering its children that you don't really want to deal with if you're building a new component.
In the old AWT world, Canvas was the base class for new components. Swing doesn't have a JCanvas, so some people make the jump to JPanel as a base class. Use JComponent instead; it's a cleaner solution.
4. Use Collections
Java 2 includes a nice set of object buckets called the Collections API. This underappreciated API lives in the java.util package and provides interfaces, classes, and utilities for working with groups of objects. You're probably familiar with Vector and Hashtable. The Collections API provides a framework that encompasses Vector, Hashtable, and several new collection classes.
Also included are static utility methods in the Collections class for sorting collections, creating threadsafe versions of collections, and other common tasks. For a full story, see the coverage in Learning Java.
5. Use Double Equals for Comparisons
This is a holdover from C. It made its way into C++, and then Java used a lot of C++ syntax. The bug goes like this: Somewhere, you accidentally type a single equals sign instead of a double one when examining a boolean value:
boolean b = false;
if (b = true) {
// Always gets executed.
}
Instead of performing a comparison, as you'd hoped, you're actually assigning true to the variable b. This assignment has an overall value of true, so the if always succeeds.
Some people suggest reversing the order of the comparison, so the literal value always comes first. This generates a compile-time error for if (true = b), so you'll figure out what's wrong and change it to if (true == b). Personally, I don't like how this looks, so I just muddle through the old fashioned way, making darn sure I always use a double equals when I need it.
6. Add Application Exit Logic
Swing frame windows (JFrames) automatically close themselves if you click on the close icon (the X in the corner). However, if the JFrame was the main window for your application, the application will not actually quit. After closing the window, users will need to hit Ctrl-C or whatever key sequence stops a running application on their particular platform. Worse, if the application was started with javaw, it will continue to run invisibly.
There's an easy fix: shut down the application when the main window closes. It looks like this:
// JFrame f;
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent we) { System.exit(0); }
});
7. Java SDK and JRE Confusion
On Windows, you may actually have two Java environments in different places on your computer. The JDK (or SDK, whatever you want to call it) is usually installed in a directory like \jdk1.2.2. The JRE, including the Java Plug-in, is typically installed in a directory like \Program Files\JavaSoft\JRE\1.2.
This becomes a problem whenever you are installing standard extension libraries or editing files like the java.security properties file. The problem I usually have goes something like this: I install a standard extension library, like the Communications API or the Java Cryptography Extension, in \jdk1.2.2\jre\lib\ext. I work on a program that uses the extension API, and it compiles fine. When I go to run it, it complains that the classes in the standard extension library are not found.
The problem is that I'm compiling using \jdk1.2.2\bin\javac.exe, but when I run the thing, it uses \winnt\java.exe, which is actually the JRE, which would expect to find the extension API in \Program Files\JavaSoft\JRE\1.2\jre\lib\ext.
To fix this, I usually remove or rename java.exe and javaw.exe in \winnt. Then when I run my program, it uses \jdk1.2.2\bin\java.exe which is the Java SDK where I installed the standard extension API.
8. Fully Load Images Using ImageIcon
You can load GIF, JPEG, and (in SDK 1.3) PNG images using Toolkit's getImage() method:
Image i = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit().getImage("tarsier.png");
However, Images use lazy data loading, so the data for the image won't start to be loaded until you try to display the image. You can use a MediaTracker to force the data to load, but it's a pain in the butt. An easier solution is to use one of ImageIcon's constructors, which does the dirty work of waiting for image data to load. Then you can just pull out the image and use it, confident in the knowledge that its data is fully loaded:
Image i = new javax.swing.ImageIcon("tarsier.png").getImage();
9. Use getResourceAsStream() For Portability
If you've got a serious application, you'll probably want to package it up in a JAR file someday for easy distribution. If your application loads image and sound resources from files, as it likely will, you may find all the resource-loading code breaks when you put your application in a JAR. To avoid this, there's a way of loading application resources that work with regular files and inside a JAR.
The straightforward, non-portable way of referencing a file looks something like this:
InputStream in = FileInputStream("images/tarsier.png");
When this code runs inside a JAR, it will still look for the file in the filesystem, rather than trying to find the image file inside the JAR. Instead, use code like this:
InputStream in = getClass().getResourceAsStream("images/tarsier.png");
This looks for images/tarsier.png relative to the location of the referenced class, and it works inside JAR files.
10. Use the Main-class JAR Attribute
If you do package up an application in a JAR, there are two ways to run it. The first way is kind of clumsy--you have to add the JAR to your CLASSPATH and you have to know the name of the class to run. Suppose, for example, that I have an application called Shorts, packages in a JAR called Shorts.jar. To run it, I'd do something like this:
java -cp Shorts.jar Shorts
A much nicer solution is to use the Main-class attribute, which is a way of embedding the name of the class to run inside the JAR. Then you can just run the application (in Java 2, at least) like this:
java -jar Shorts.jar
How do you do it? Normally, you would create the JAR something like this:
jar cvf Shorts.jar *.class
The trick to adding the Main-class attribute is defining an entirely separate file with the attribute definition. For instance, create the following one-line file and save it as extra.mf:
Main-class: Shorts
Now, to create the JAR, use this command line:
jar cvmf extra.mf Shorts.jar *.class
The m option reads information from the extra.mf file you just created and adds it to the manifest of the JAR you're creating. Now you can run the JAR using java -jar Shorts.jar.
ANCIENT MULTIPLICATION






One of the earliest records of multiplication is the method shown in the Rhind Papyrus. The method used a process of doubling that as in this brief example of 22 x 44= 968. First we write down the numbers 1 and 44, then we double each number and write the results under the originals. This is continued until the next number on the left side would exceed 22.
1------44
2-------88+
4-----176+
8-----352
16----704+
At this point we start down the left side looking for a total of 22. Each time we can add the number without exceeding our goal of 22, we put a check mark by the number opposite (I have used a plus sign instead). To total 23 we take the 16 first. Since 16+8 > 22 we omit 22 and move to the 4, and two. Since 16+4+2=22, we mark, and then sum, the values adjacent to these numbers. The result, 88 + 176 + 704 = 968.
A copy of the Rhind Papyrus with the Egyptian method can be found at the University of St. Andrews Math History web site. It includes how the same method is used for division and additional material about Egyptian fraction techniques.
According to Bea Lumpkin Algebra Activities from Many Cultures, Egyptians also would use a multiple of ten and then doubles of that if needed. For instance in the problem above they may have started by putting down 10---440 and 20---880 and then continuing with 1---44 and 2---88 and found 22*44 by adding 880 + 88.
The method is often confused with a similar approach known as Russian Peasant Multiplication. In the Russian method the two factors are written, and then one is doubled as the other is halved. This method is sometimes called duplation and mediation (doubling and halving) in some early arithmetic texts. The same 22*44 example from above would look like this:
22----44
11----88+
5----176+
2----352
1----704+
In this procedure the doubled number (right column) is marked each time the halved column is an odd number. Note that when there is a remainder or fraction it is ignored. Notice that the marked numbers are identical to the ones marked in the Egyptian method above. You can find a nice article with explanations of the binary nature of this method at the Dr. Math FAQ on the topic.
A third method that seems to have been created by Hindu mathematicians is called lattice, cell, or gelosie (from the name of a type of shutter, now spelled jalousie) multiplication. This method was known at least as early as 1010 when the Persian scholar, Karaji (ka-ra-yee) demonstrated it in his Kafi fil Hisab, (Book of Satisfactions). This method is very similar to the modern algorithm, except that the alignment is in a rectangle, and the additions are carried out along a diagonal row.
This figure shows an example of one method using 132 x 247.
The factors are written along the top and right side. In many early Arabic and other examples the numbers were frequently written right to left. The multiplication of 7 times 2 is shown in the bottom right corner with the tens moved to the shaded column. This is repeated in 7x3 = 21 in the next column to the left. Notice that with this method it made no difference if you started from units to hundreds or hundreds to units since each product had two spaces for an answer. The results of the multiplications were added along the diagonals which are shaded to make alignment easier in the figure. In the figure the shaded diagonal at the bottom right shows 8+1+1=10. The ten is written by spreading the number over two columns. The arrow shows the carry digit. The numbers in the boxes are final results with arrows indicating when a ten value was carried to the next column. Many teachers use this today as an alternative to the traditional algorithm, but it seems to offer few advantages in terms of understanding the nature of multiplication. You can find additional examples and explanation here.
A method that should look very familiar to most people was used by the Indian mathematician Brahmagupta during the eleventh century. The method is referred to as gomutrika, which seems to translate to "trajectory of a cow's urine". Brahmagupta wrote one of the factors horizontally and repeatedly along a skew line for each digit of the second factor. This second factor he wrote down the page. Here is how he might have written out 315 x 452.
The notations in italics at the right are added to show the steps, and were not part of the original. Although the alignment in this example goes right to left, he also wrote variations with the shift moving to the left from row to row.
Another type of multiplication used in earlier days is shown in the first arithmetic book published in North America, the Sumario compendioso de las quentas de plata y oro que in los reynos del Piru son necessarias a los mercaderes y todo genero de tratantes Los algunas reglas tocantes al Arithmetica. The title translates to "Comprehensive Summary of the counting of silver and gold, which, in the kingdoms of Peru, are necessary for merchants and all kinds of traders". The author was Brother Juan Diez, a priest who arrived in Mexico with Cortez in 1519 but the book was not published until 1556. I have attempted to duplicate in type a figure from an article Spanish colonial Mathematics: A Window on the Past by Ed Sandifer that I found on Dr. Sandifer's webpage. I will show several steps of the development to facilitate the readers understanding.
The problem is to multiply 875 by 978. Multiplication starts from the left, and the 800 is multiplied by the 900.
Notice that the zeros are left off, much as we leave them off now when we start from the other side. Next the 800 is multiplied by the 70 in 978. Since this has one less power of ten than the previous multiple, it will start one column to the right, so the 5 of the 56 goes under the 2 of the 72, but since there is nothing in the third column, the 6 goes at the top of this column, next to the 2 of the 72.
The next multiplication is between the 800 and the 8 in 978, which is again one less power than the previous multiple, and so the 6 in the 64 must go in the column under the 6 of the previous 56. The 4 will go at the top of the next column since there is nothing in that column yet.
Now that all three digits of 978 have been multiplied by the 8(hundred), we move on to the 7 in 875 and multiply it across. Since the 70 times 900 will have only one less place than the 800 times 900, it will start in the second column also, so the 6 of the 63 will go under the 2 and 5 in the second column, and the 3 will go under the pair of sixes in the third column.
From here we hope the reader can follow on his own, and we show the completed problem.
the reader might wish to compare the appearance of this method to the Galley division method. It is not hard to imagine that this multiplication was even easier to perform on a sand tray or counting table where numbers were simply added and adjusted as the work progressed
Certainly one of the first counting methods involved the use of the hands, and probably simple multiplication methods were likewise commonly performed on the hands. The image at right shows the method of finger counting as used in the Summa Arithmetica by Pacioli (1532). Similar figures are described and illustrated back to the birth of Christ. In Menninger's Number Words and Number Symbols(pg 211) he shows an image of 1st Century Roman Markers used in a game which show the numbers eight and nine both in Roman Numerals and in finger gestures. The counters are located in the British Museum. Pliny the Elder, who died in 79AD, wrote of a statue of Janus in Rome which showed the finger sign for 300 on the right hand and 65 on the left, to indicate the number of days in the year. The representation of numbers greater than 100 on the right hand led to the reference by the Roman Author Juvenal, around 100 AD, about Nestor, the oldest of the Greek kings at the Battle of Troy; "Happy is he who so many times over the years has cheated death and now reckons his age on hte right hand."
Counting on the fingers is not the same as multiplying, but there can be no doubt that it was around by the time that Leonardo of Pisa wrote, "multiplication with the fingers must be practices constantly, so that the mind like the hands becomes more adept at adding and multiplying various numbers. (from Menninger as above, pg218)
One simple hand multiplication is now so wide-ranging that it is hard to believe it was not known prior to the first written description. The method is used to replace learning the multiplication tables from six to nine. To use the system, raise both hands before the face and think of the digits as the excess over five. To multiply 7 x 8, turn down two digits on the left hand (thumb and first finger) since 7 is 2 in excess of five. Now turn down the first three fingers leaving only the little finger and ring finger extended on the right hand. To find the product of 7 and 8, count the number of fingers turned down. Two and three are five, so the ten's digit is five for fifty. now multiply the fingers extended on each hand; two times three is six so the units digit is six, and the answer is fifty-six.
Essentially the same method is explained in Robert Recorde's Grounde of Artes(about 1543). The image on the right is from Cajori's A History of Mathematical Notations . The instructions are to multiply the compliments on the right to get the units digit, then take either of the original factors (7 or 8) and subtract the compliment of the other joined by a line, for example 8-3, to get the ten's digit. Some suggest this is the origin of the use of an X for multiplication.
Another old method of hand multiplication still found in use is the multiply by nine device. Hold both hands in front of the body with the palms toward you. To multiply nine by any number less than nine, for instance four, count in on the fingers from left to right and turn down the fourth digit. The three still standing on the left are the number of tens, the six on the right of the turned digit are the ones. The method also can be extended to multiples of 9 up through 19 by the same motions. For example, to multiply 9 x 14, bend the same finger as in 9 x 4. Now instead of three tens, add nine to the digits shown to get 12 tens or 120, and the six still standing on the right make 126. If that explanation is not clear, you can see a much longer explanation with photos of the hands here .
In the 15th Century Multiplication was presented in various, often similar, algorithms. In his Capitalism and Arithmetic, Frank Swetz lists eight different methods that appear in the 1494 work of Luca Pacioli:
The first is very similar to the gelosie method demonstrated above. It probably was originally modeled on a method using markers on a squared grid similar to a chess board. The difference was that the multiplier was written down the side on a diagonal, thus forcing the indexing of the partial products, and the carry digits were transferred from column to column mentally. This may have often been used with the "by the table" method so that partial products could be formed from values looked up in the tables. I have not seen the "little castle method of multiplication, but suspect it was similar to the method illustrated on page 441 of Menniger. This is essentially an upside down version of the method above from the "Sumario", the early Spanish language arithmetic. "Per Quadrilatero" was another chessboard method, usually written in squares and was essentially the gelosie method but the carries were done mentally so the diagonal lines were not found.
Per Crocetta is another candidate for the origin of the x as a symbol for multiplication. The first illustration shows how the figures were often written and shows the multiplication of 34 and 62. The lines shown should be familiar to any algebra student who has memorized the "FOIL" method for finding a product. At first all four products were probably written out below and indexed as needed to be added in columns. Later the idea of carrying from one product into another probably produced the current version. Many books printed the same operation with only the cross shown in the second figure according to Swetz. He also mentions that Pacioli extended this method to more than two digits in the factors.
Per Repiego was a multiplication that broke one of the multipliers into its factors and then multiplied by these. 35 x 14 might be multiplied by breaking 14 into 2x7 and then multiplying each of these times 35 and adding the two results. I have also not seen an example of the scapezza method, but assume it simply was a version of one of the chessboard methods which was seperated out instead of kept in the framework of the chessboard.
Sunday, March 21, 2010
STETHOSCOPE
The stethoscope was invented by the French physician R.T.H. Laënnec. René Théophile Hyacinthe Laënnec is generally considered to be the father of chest medicine.
History of the Stethoscope
The history of the monaural stethoscope and the binaural stethoscope.
Docteur Laennec
One day in 1816, Laennec is invited by urchins to hear to the scratching of a pin transmitted through the length of a wooden beam. He is thereby inspired to fashion a paper tube to listen to the chests of his patients.
History of the Stethoscope
The history of the monaural stethoscope and the binaural stethoscope.
Docteur Laennec
One day in 1816, Laennec is invited by urchins to hear to the scratching of a pin transmitted through the length of a wooden beam. He is thereby inspired to fashion a paper tube to listen to the chests of his patients.
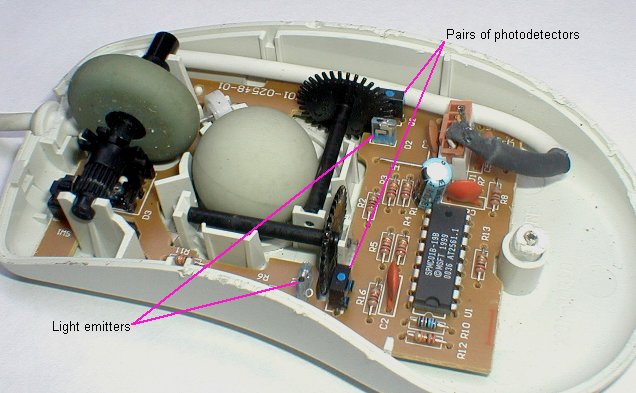
INVENTION OF MOUSE
In 1964, the first prototype computer mouse was made to use with a graphical user interface (GUI), 'windows'. Engelbart received a patent for the wooden shell with two metal wheels (computer mouse U.S. Patent # 3,541,541) in 1970, describing it in the patent application as an "X-Y position indicator for a display system." "It was nicknamed the mouse because the tail came out the end," Engelbart revealed about his invention. His version of windows was not considered patentable (no software patents were issued at that time), but Douglas Engelbart has over 45 other patents to his name.
Throughout the '60s and '70s, while working at his own lab (Augmentation Research Center, Stanford Research Institute), Engelbart dedicated himself to creating a hypermedia groupware system called NLS (for oNLine System). Most of his accomplishments, including the computer mouse and windows, were part of NLS.
In 1968, a 90-minute, staged public demonstration of a networked computer system was held at the Augmentation Research Center -- the first public appearance of the mouse, windows, hypermedia with object linking and addressing, and video teleconferencing.
Douglas Engelbart was awarded the 1997 Lemelson-MIT Prize of $500,000, the world's largest single prize for invention and innovation. In 1998, he was inducted into the National Inventors Hall of Fame.
Currently, Douglas Engelbart is the director of his company, Bootstrap Institute in Fremont, California, which promotes the concept of Collective IQ. Ironically, Bootstrap is housed rent free courtesy of the Logitech Corp., a famous manufacturer of computer mice.
Throughout the '60s and '70s, while working at his own lab (Augmentation Research Center, Stanford Research Institute), Engelbart dedicated himself to creating a hypermedia groupware system called NLS (for oNLine System). Most of his accomplishments, including the computer mouse and windows, were part of NLS.
In 1968, a 90-minute, staged public demonstration of a networked computer system was held at the Augmentation Research Center -- the first public appearance of the mouse, windows, hypermedia with object linking and addressing, and video teleconferencing.
Douglas Engelbart was awarded the 1997 Lemelson-MIT Prize of $500,000, the world's largest single prize for invention and innovation. In 1998, he was inducted into the National Inventors Hall of Fame.
Currently, Douglas Engelbart is the director of his company, Bootstrap Institute in Fremont, California, which promotes the concept of Collective IQ. Ironically, Bootstrap is housed rent free courtesy of the Logitech Corp., a famous manufacturer of computer mice.
PYRAMIDS
Ancient Egypt was the home of one of the most advanced civilizations of its time.
Today, many historians are held in our memories in statues and paintings. However, the Ancient Egyptian Leaders held themselves in memory in a different way. Obsessed with the afterlife, years ago Egyptian rulers ordered thousands of slaves to move stone and rocks forming what we call today, the Pyramids. The pyramids were created to assist the kings of their time in walking on through the afterlife.
The beginning of the Old Kingdom is believed to be the construction of Djoser's monument. The construction project of Pharaoh Djoser's Step Pyramid started around 2620 B.C. It was created to amaze the ancient Egyptians, and amaze them is exactly what it did. The Step Pyramid rises to a height of 60 meters. Its base being 120 meters by 108 meters. Inside is a system of underground corridors and rooms. The main feature of the Step Pyramid is a central shaft 25 meters deep and 8 meters wide.
However, Djoser's pyramid was not exactly a pyramid. It was made more like steps, and not smooth on all sides like other pyramids. As the pyramids evolved, there where failures. Glorious failures, until they finally got the design just right. The first smooth sided, true pyramid was built at Meidum. When Snefru took the throne sometime near 2575 BC, Djoser's Step Pyramid was the only large royal pyramid that was completed. Snefru then became the greatest pyramid builder in Egyptian history by completing not one pyramid, but three. Many believe that building Djoser's pyramid, which was done by hundreds of workers, served to join the provinces into the world's first nation-state. During the Old Kingdom, which began around 2700 BC and lasted some 550 years, each pharaoh after Djoser marshaled a vast portion of his country's manpower and wealth to build his own tomb and ensure his immortality.
Two generations after Djoser's reign, the center of the Old Kingdom moved to the barren plateau of Giza. Three 4th dynasty pyramids were erected here; they are included among the Seven Wonders of the World. The one the farthest north and the oldest was built by Khufu (2558-2532 BC), the second king during the 4th dynasty. It was called the Great Pyramid. The middle pyramid was built by Khafre (2520 - 2494 BC), the fourth king of the 4th dynasty. The southern and last pyramid to be construction was of Menkaure (2532-2503 BC), the sixth king of the 4th dynasty.
Near 2465 B.C, about halfway through the Old Kingdom, pyramids suddenly became less important. No one knows why, but many scholars have suggested that after Khufu's pyramid, which took roughly 23 years to build, the kingdom grew weary with each Pharaoh's effort to outdo the last, several pharaohs died before the completion of their pyramids. A king would never again build a pyramid on a truly colossal scale. Instead the religious focus shifted from the pyramid itself toward the mortuary temple that stood to the east of it. As the culture grew more sophisticated, even the Pharaoh's unlimited power was beginning to fade.
To this very day, we continue to look in awe at the amazing marvels. For many years onward, they will remain important to all who see them. Just is it was important so many years ago.
Today, many historians are held in our memories in statues and paintings. However, the Ancient Egyptian Leaders held themselves in memory in a different way. Obsessed with the afterlife, years ago Egyptian rulers ordered thousands of slaves to move stone and rocks forming what we call today, the Pyramids. The pyramids were created to assist the kings of their time in walking on through the afterlife.
The beginning of the Old Kingdom is believed to be the construction of Djoser's monument. The construction project of Pharaoh Djoser's Step Pyramid started around 2620 B.C. It was created to amaze the ancient Egyptians, and amaze them is exactly what it did. The Step Pyramid rises to a height of 60 meters. Its base being 120 meters by 108 meters. Inside is a system of underground corridors and rooms. The main feature of the Step Pyramid is a central shaft 25 meters deep and 8 meters wide.
However, Djoser's pyramid was not exactly a pyramid. It was made more like steps, and not smooth on all sides like other pyramids. As the pyramids evolved, there where failures. Glorious failures, until they finally got the design just right. The first smooth sided, true pyramid was built at Meidum. When Snefru took the throne sometime near 2575 BC, Djoser's Step Pyramid was the only large royal pyramid that was completed. Snefru then became the greatest pyramid builder in Egyptian history by completing not one pyramid, but three. Many believe that building Djoser's pyramid, which was done by hundreds of workers, served to join the provinces into the world's first nation-state. During the Old Kingdom, which began around 2700 BC and lasted some 550 years, each pharaoh after Djoser marshaled a vast portion of his country's manpower and wealth to build his own tomb and ensure his immortality.
Two generations after Djoser's reign, the center of the Old Kingdom moved to the barren plateau of Giza. Three 4th dynasty pyramids were erected here; they are included among the Seven Wonders of the World. The one the farthest north and the oldest was built by Khufu (2558-2532 BC), the second king during the 4th dynasty. It was called the Great Pyramid. The middle pyramid was built by Khafre (2520 - 2494 BC), the fourth king of the 4th dynasty. The southern and last pyramid to be construction was of Menkaure (2532-2503 BC), the sixth king of the 4th dynasty.
Near 2465 B.C, about halfway through the Old Kingdom, pyramids suddenly became less important. No one knows why, but many scholars have suggested that after Khufu's pyramid, which took roughly 23 years to build, the kingdom grew weary with each Pharaoh's effort to outdo the last, several pharaohs died before the completion of their pyramids. A king would never again build a pyramid on a truly colossal scale. Instead the religious focus shifted from the pyramid itself toward the mortuary temple that stood to the east of it. As the culture grew more sophisticated, even the Pharaoh's unlimited power was beginning to fade.
To this very day, we continue to look in awe at the amazing marvels. For many years onward, they will remain important to all who see them. Just is it was important so many years ago.
HISTORY OF PYTHAGORAS


The History of Pythagoras and his Theorem
In this section you will learn about the life of Pythagoras and how it is that the theorem is known as the Pythagorean Theorem.
Be aware that there are no good records about the life of Pythagoras, so the exact dates and other issues are not known with certainty. In addition, the names of some of the people as well as the places where Pythagoras lived may have different spellings.
Pythagoras was born in the island of Samos in ancient Greece1. There is no certainty regarding the exact year when he was born, but it is believed that it was around 570 BC That is about 2,570 years ago! Those were times when a person believed in superstitions and had strong beliefs in gods, spirits, and the mysterious. Religious cults were very popular in those times.
Pythagoras of Samos
Pythagoras' father's name was Mnesarchus and may have been a Phoenician. His mother's name was Pythais. Mnesarchus made sure that his son would get the best possible education. His first teacher was Pherecydes, and Pythagoras stayed in touch with him until Pherecydes' death. When Pythagoras was about 18 years old he went to the island of Lesbos where he worked and learned from Anaximander, an astronomer and philosopher, and Thales of Miletus, a very wise philosopher and mathematician.
Thales had visited Egypt and recommended that Pythagoras go to Egypt. Pythagoras arrived in Egypt around 547 BC when he was 23 years old. He stayed in Egypt for 21 years learning a variety of things including geometry from Egyptian priests . It was probably in Egypt where he learned the theorem that is now called by his name.
By the time he was about 55 years old he returned to his native land and started a school on the island of Samos. However, because of the lack of students he decided to move to Croton in the south of Italy.
In Croton he started a school which concentrated in the teaching and learning of Mathematics, Music, Philosophy, and Astronomy and their relationship with Religion. It is said that as many as 600 of the worthiest people in the city attended the school, including Theana whom he married when he was 60. The school reached its highest splendor around the year 490 BC. He taught the young to respect their elders and to develop their mind through learning. He emphasized justice based on equality. Calmness and gentleness were principles encouraged at the school. Pythagoreans became known for their close friendships and devotion to each other. More than anyone before him Pythagoras combined the spiritual teachings with the pursuit of knowledge and science.
Pythagoras also headed a cult known as the secret brotherhood that worshiped numbers and numerical relationships. They attempted to find mathematical explanations for music, the gods, the cosmos, etc. Pythagoras believed that all relations could be reduced to number relations.
At some point Pythagoras was exiled from Croton and had to move to Tarentum. After 16 years he had to move again, this time to Metapontus where he lived four years before he died at the age of 99.
Here we have a picture of a statue of Phytagoras in the island of Samos. If you click on the figure you'll be able to see a larger picture. On the bottom of the statue the text is "". The literal translation is "Pythagoras the Samosan", but the preferred translation is "Pythagoras of Samos".
Now let's talk a bit about the theorem that bears his name. The Egyptians knew that a triangle with sides 3, 4, and 5 make a 90o angle. As a matter of fact, they had a rope with 12 evenly spaced knots like this one:
that they used to build perfect corners in their buildings and pyramids. It is believed that they only knew about the 3, 4, 5 triangle and not the general theorem that applies to all right triangles.
The Chinese also knew this theorem. It is attributed to Tschou-Gun who lived in 1100 BC. He knew the characteristics of the right angle. The theorem was also known to the Caldeans and the Babylonians more than a thousand years before Pythagoras. A clay tablet of Babylonian origin was found with the following inscription: "4 is the length and 5 the diagonal. What is the breadth?"
So why is it called the Pythagorean Theorem? Even though the theorem was known long before his time, Pythagoras certainly generalized it and made it popular. It was Pythagoras who is attributed with its first geometrical demonstration. That is why it is known as the Pythagorean Theorem. There are hundreds of purely geometric demonstrations as well as an unlimited (that is right -- an infinite number) of algebraic proofs.
The Pythagorean Theorem is one of the most important theorems in the whole realm of geometry. We will conclude this section by stating the theorem in words:
The square described upon the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle is equal to the sum of the squares described upon the other two sides.
Another way of saying the same thing is:
When the two shorter sides in a right triangle are squared and then added, the sum equals the square of the longest side or hypotenuse.
LARGEST EARTHQUAKES SINCE 1990
Location Date UTC Magnitude Lat. Long. Reference
1. Chile 1960 05 22 9.5 -38.29 -73.05 Kanamori, 1977
2. Prince William Sound, Alaska 1964 03 28 9.2 61.02 -147.65 Kanamori, 1977
3. Off the West Coast of Northern Sumatra 2004 12 26 9.1 3.30 95.78 Park et al., 2005
4. Kamchatka 1952 11 04 9.0 52.76 160.06 Kanamori, 1977
5. Offshore Maule, Chile 2010 02 27 8.8 -35.846 -72.719 PDE
6. Off the Coast of Ecuador 1906 01 31 8.8 1.0 -81.5 Kanamori, 1977
7. Rat Islands, Alaska 1965 02 04 8.7 51.21 178.50 Kanamori, 1977
8. Northern Sumatra, Indonesia 2005 03 28 8.6 2.08 97.01 PDE
9. Assam - Tibet 1950 08 15 8.6 28.5 96.5 Kanamori, 1977
10. Andreanof Islands, Alaska 1957 03 09 8.6 51.56 -175.39 Johnson et al., 1994
11. Southern Sumatra, Indonesia 2007 09 12 8.5 -4.438 101.367 PDE
12. Banda Sea, Indonesia 1938 02 01 8.5 -5.05 131.62 Okal and Reymond, 2003
13. Kamchatka 1923 02 03 8.5 54.0 161.0 Kanamori, 1988
14. Chile-Argentina Border 1922 11 11 8.5 -28.55 -70.50 Kanamori, 1977
15. Kuril Islands 1963 10 13 8.5 44.9 149.6 Kanamori, 1977
Updated 2010 March 01
1. Chile 1960 05 22 9.5 -38.29 -73.05 Kanamori, 1977
2. Prince William Sound, Alaska 1964 03 28 9.2 61.02 -147.65 Kanamori, 1977
3. Off the West Coast of Northern Sumatra 2004 12 26 9.1 3.30 95.78 Park et al., 2005
4. Kamchatka 1952 11 04 9.0 52.76 160.06 Kanamori, 1977
5. Offshore Maule, Chile 2010 02 27 8.8 -35.846 -72.719 PDE
6. Off the Coast of Ecuador 1906 01 31 8.8 1.0 -81.5 Kanamori, 1977
7. Rat Islands, Alaska 1965 02 04 8.7 51.21 178.50 Kanamori, 1977
8. Northern Sumatra, Indonesia 2005 03 28 8.6 2.08 97.01 PDE
9. Assam - Tibet 1950 08 15 8.6 28.5 96.5 Kanamori, 1977
10. Andreanof Islands, Alaska 1957 03 09 8.6 51.56 -175.39 Johnson et al., 1994
11. Southern Sumatra, Indonesia 2007 09 12 8.5 -4.438 101.367 PDE
12. Banda Sea, Indonesia 1938 02 01 8.5 -5.05 131.62 Okal and Reymond, 2003
13. Kamchatka 1923 02 03 8.5 54.0 161.0 Kanamori, 1988
14. Chile-Argentina Border 1922 11 11 8.5 -28.55 -70.50 Kanamori, 1977
15. Kuril Islands 1963 10 13 8.5 44.9 149.6 Kanamori, 1977
Updated 2010 March 01
Saturday, March 13, 2010
SUBMARINE VOLCANOES
Name Elevation Location Last known eruption
meters feet Coordinates
Adams Seamount -59 -194 25.37°S 129.27°W 50 BC ± 1000 years
Axial Seamount -1400 -4592 45.55°N 130.00°W 1998
Banua Wuhu -5 -16 3.138°N 125.491°E 1919
Bear Seamount -1100 -3609 39.92°N 67.4°W -
Bowie Seamount -24 -79 53.3°N 135.63°W 18,000 BP
Campi Flegrei Mar Sicilia -8 -26 1867
Dequey -24 - 20.33°N 121.75°E 1854
Dom João de Castro Bank -14 -46 38.23°N 26.63°W 1720
Empedocles -7 -23
Emperor of China -2850 -9350 6.62°S 124.22°E -
Foundation Seamounts
Ferdinandea -6 -20 1863
Healy -1150 -3772 34.98°S 179.00°W 1360
Kick-'em-Jenny -160 -525 12.30°N 61.64°W 2001
Kolumbo -10 -33 1650
Kuwae 16.85°S 168.52°E
Loihi Seamount -969 -3178 18.92°N 155.27°W 1996
Moai
Monaco Bank -197 -646 37.6°N 25.88°W 1911
Monowai Seamount -100 -328 25.887°S 177.188°W 2006
Myōjin-shō -50 -164
Nieuwerkerk -2285 -7497 6.60°S 124.675°E -
Protector Shoal -27 -90 1962
Pukao
Rumble I -1100 -3610 35.5°S 178.9°E -
Rumble II -880 -2890 35.4°S 178.6°E -
Rumble III -140 -459 35.745°S 178.478°E 1986
Rumble IV -450 -1476 36.13°S 178.05°E -
Rumble V -1100 -3610 36.139°S 178.197°E -
Submarine 1922 -5000 -16404 3.97°N 124.17°E -
Supply Reef -8 -26 20.13°N 145.1°E 1989
Tuzo Wilson Seamounts - - 51.4°N 130.9°W Holocene
Vailulu'u -590 -1935
Yersey -3800 -12467 7.53°S 123.95°E -
meters feet Coordinates
Adams Seamount -59 -194 25.37°S 129.27°W 50 BC ± 1000 years
Axial Seamount -1400 -4592 45.55°N 130.00°W 1998
Banua Wuhu -5 -16 3.138°N 125.491°E 1919
Bear Seamount -1100 -3609 39.92°N 67.4°W -
Bowie Seamount -24 -79 53.3°N 135.63°W 18,000 BP
Campi Flegrei Mar Sicilia -8 -26 1867
Dequey -24 - 20.33°N 121.75°E 1854
Dom João de Castro Bank -14 -46 38.23°N 26.63°W 1720
Empedocles -7 -23
Emperor of China -2850 -9350 6.62°S 124.22°E -
Foundation Seamounts
Ferdinandea -6 -20 1863
Healy -1150 -3772 34.98°S 179.00°W 1360
Kick-'em-Jenny -160 -525 12.30°N 61.64°W 2001
Kolumbo -10 -33 1650
Kuwae 16.85°S 168.52°E
Loihi Seamount -969 -3178 18.92°N 155.27°W 1996
Moai
Monaco Bank -197 -646 37.6°N 25.88°W 1911
Monowai Seamount -100 -328 25.887°S 177.188°W 2006
Myōjin-shō -50 -164
Nieuwerkerk -2285 -7497 6.60°S 124.675°E -
Protector Shoal -27 -90 1962
Pukao
Rumble I -1100 -3610 35.5°S 178.9°E -
Rumble II -880 -2890 35.4°S 178.6°E -
Rumble III -140 -459 35.745°S 178.478°E 1986
Rumble IV -450 -1476 36.13°S 178.05°E -
Rumble V -1100 -3610 36.139°S 178.197°E -
Submarine 1922 -5000 -16404 3.97°N 124.17°E -
Supply Reef -8 -26 20.13°N 145.1°E 1989
Tuzo Wilson Seamounts - - 51.4°N 130.9°W Holocene
Vailulu'u -590 -1935
Yersey -3800 -12467 7.53°S 123.95°E -
TSUNAMI WAVES
Tsunamis are often confused with many other types of waves. Here are descriptions of the different kinds:
tidal wave - These waves are caused by the moon’s gravitational attraction. They are generally only a few feet high, although higher waves are found during the new and full moons. They can rise 5 to 6 feet above normal when the new and full moon occurs at the same time as the moon’s perigee (the time when the moon is closest to the earth). Tidal waves are harmless unless accompanied by storm conditions or on unusual coastlines, where the topography creates daily tides as high as 50 feet.
tidal bore - These are quickly advancing front waves of incoming tides and are found in shallow estuaries. It is usually a foaming water wall that signals approaching tides. The height can vary from a few inches to a few feet, depending on the tide’s strength, the attraction of the moon, and the geography of the estuary. In the Tsientang River in China, bores have been recorded at 25 feet traveling 13 knots.
internal waves/underwater waves - These are the strong, vertical motions that a current causes. They usually occur when the current is passing through a narrow passage between a pair of islands, diving into a deep ocean trench, or when two underwater currents of differing density merge together. One can detect internal waves from the surface by noting patch of strong turbulence, which can extend as long as 125 miles. Beneath the ocean surface, the wave, or water of different density, can measure as high as 300 feet. Some experts think that these are responsible for the disappearance of some submarines, causing them to drop below safe traveling depths.
storm waves/sea surges - These are wind-driven waves created on top of normal tides, and are often caused by hurricanes and cyclones. They reach 30 to 40 feet in height, producing a constant pounding motion as opposed to the tsunami’s characteristic single huge wave.
seiche - This is the rhythmic vibration of water in an enclosed water body. Water moves slowly back and froth from shore to shore in waves no higher than 5 feet. They are created by either seismic action or storms.
tidal wave - These waves are caused by the moon’s gravitational attraction. They are generally only a few feet high, although higher waves are found during the new and full moons. They can rise 5 to 6 feet above normal when the new and full moon occurs at the same time as the moon’s perigee (the time when the moon is closest to the earth). Tidal waves are harmless unless accompanied by storm conditions or on unusual coastlines, where the topography creates daily tides as high as 50 feet.
tidal bore - These are quickly advancing front waves of incoming tides and are found in shallow estuaries. It is usually a foaming water wall that signals approaching tides. The height can vary from a few inches to a few feet, depending on the tide’s strength, the attraction of the moon, and the geography of the estuary. In the Tsientang River in China, bores have been recorded at 25 feet traveling 13 knots.
internal waves/underwater waves - These are the strong, vertical motions that a current causes. They usually occur when the current is passing through a narrow passage between a pair of islands, diving into a deep ocean trench, or when two underwater currents of differing density merge together. One can detect internal waves from the surface by noting patch of strong turbulence, which can extend as long as 125 miles. Beneath the ocean surface, the wave, or water of different density, can measure as high as 300 feet. Some experts think that these are responsible for the disappearance of some submarines, causing them to drop below safe traveling depths.
storm waves/sea surges - These are wind-driven waves created on top of normal tides, and are often caused by hurricanes and cyclones. They reach 30 to 40 feet in height, producing a constant pounding motion as opposed to the tsunami’s characteristic single huge wave.
seiche - This is the rhythmic vibration of water in an enclosed water body. Water moves slowly back and froth from shore to shore in waves no higher than 5 feet. They are created by either seismic action or storms.
YOUTUBE VIDEOS

We’ve been hearing for some time (starting with an ex-Youtube employee) that the number of video streams per day reported by Comscore, Nielsen and other metrics services way under-report on Youtube’s total video streams.
It’s hard to compare apples to apples, though. Recent Comscore data says Google/YouTube streams just under 7 billion videos per month in the U.S., up from around 5 billion/month late last year. That’s about 225 million streams a day, which still puts them well above all the next major competitors (MySpace, Hulu, Yahoo, Viacom, Microsoft, etc.). Nielsen says Google/YouTube streams 5.5 billion videos/month in the U.S.
But the real number of streams/day, we’ve now confirmed with a source at Google, is above 1.2 billion/day worldwide. That matches what we’ve heard from other sources. That pretty much means everyone on the Internet, on average, is watching one YouTube video per day.
Google hasn’t commented on this in the past, and we can’t figure out exactly why. It may have to do with ongoing litigation and the desire to keep exact numbers quiet. Or it may be that they don’t necessarily want analysts to have deep insight into YouTube’s true cost structure.
We’ve spoken to Comscore about this casually in the past, and they’ve noted that their estimates are based on available data, and that data doesn’t involve direct access to YouTube servers. Some companies choose to give Comscore deep access, others don’t. The data quality suffers accordingly.
But one thing is clear. Comscore thinks the total online video space is around 17 billion monthly streams in the U.S. We now know that YouTube alone serves that many video streams every fifteen days or so worldwide. Time to revise those numbers up – if YouTube has 40% of the online market share for video like Comscore says (it may actually be much higher market share, another reason Google may not want this data out there), that means the total number of video streams on the Internet is approaching 80 billion/month, a heady number.
We’ve approached MySpace and Hulu, the no. 2 and no. 3 online video services, for their exact streaming numbers. So far, no response.
SAP TRICKS
mySAP Tips & Tricks
You may have noticed that in ECC the services for object button (Generic Object Services - GOS) is missing from the sales order. This can be useful to find related IDOCS but was taken off in 4.7 due to performance reasons. If you set user profile/parameter SD_SWU_ACTIVE to X by going to SYSTEM-USERPRFOLE-OWNDATA the button will be available to you again.
SAP R/3 Tips & Tricks
Logging on without being authorized
Client 066 usually exists in a SAP system due to EarlyWatch services. Often this client does not have master users. If it is true, anyone can log into the system using the client 066, user SAP*, and password PASS. Enjoy yourself.
Special copy and paste
Click on the area and press CTRL+Y. It allows you to copy many lines at once and paste them afterwards.
Long messages on footer
Click on the message and hold the mouse button. After moving the mouse to the left side.
Direct input logs
The transaction BMV0 (direct input logs) shows all direct input logs.
Graphics on SAPscript
The program RSTXLDMC can be used to upload graphics (file extension .tif on PC files) into individual standard text.
Adding icons
Check the icon code using transaction ICON. A technical view can be found at the include named �ICON�. Sequences of characters begin and finish with the symbol @. Even plain files under operating system can contain those strings.
Filling up an empty date field quickly
Strike the key F4 (or click on matchcode symbol) and press ESCAPE. The current date is automatically set.
Setting up module FI/CO without using IMG
Almost all parameters can be set using the transactions ORFA (Asset Accounting), ORFB (Financial Accounting), and ORKS (Cost Center Accounting).
Displaying check object when not authorized
Soon after the lock try to access the transaction SU53. It reports the last objects verified and also the respective values.
Table analyses between two systems
The contents of a table between two systems can be checked through the transaction OY19.
Correction and transport system
The transaction SE10 provides the easiest way to manage any request/transport and corrections.
General command field formats
/n Skip to the next record if you are processing one batch input session
/bend Cancel a batch input foreground process
/nend Close all R/3 sessions and logoff
/nxxxx Call the transaction xxxx in the same session
/o Generate a session list
/oxxxx Call the transaction xxxx in an additional session
/i Delete the current session
/h Turn the debug mode on
/$tab Reset all buffers (for System Administrators)
/$sync Synchronize instances buffers (for System Administrators)
Report command field formats
%pri Print the current report
%pc Download the current report
%sc Call the find function
p+ Go to the next page
p- Go to the previous page
p++ Go to the last page
p-- Go to the first page
Helpful reports
RSCLTCOP Copy tables across clients
RSAVGL00 Table adjustment across clients
RSINCL00 Extended program list
RSBDCSUB Release batch-input sessions automatically
RSTXSCRP Transport SAPscript files across systems
RSORAREL Get the Oracle Release
RGUGBR00 Substitution/Validation utility
RSPARAM Display all instance parameters
RSUSR003 Check the passwords of users SAP* and DDIC in all clients
RSUSR006 List users last login
Unconditional mode when importing or exporting a request/transport
Run the command R3trans -u under user �SysID�adm.
Main return codes of tp program
0 Successfully done
4 Warnings occurred
8 Errors occurred
12 Fatal errors occurred
16 Internal errors occurred
Scheduling of system maintenance jobs
RSBTCDEL Clean the old background job records
RSDBCREO Clean batch input session log
RSPO0041 Removing old spooling objects
RSSNAPDL Clean the old ABAP error dumps
Locking the whole system
Using the command tp locksys �SysID� only the user SAP* will be allowed to login. The command tp unlocksys �SysID� cancels the lock.
Connection between SAP R/3 and operating system
The command sapevt can be used to trigger an event from the operation system. Thus, a job previously defined within R/3 will be released.
SQL code help
Run the command oerr ora �error number� under user ora�SysID�.
Oracle import and export explanations
Run the command imp help=yes under user ora�SysID�. This format can also be used with exp, impst, and expst.
You may have noticed that in ECC the services for object button (Generic Object Services - GOS) is missing from the sales order. This can be useful to find related IDOCS but was taken off in 4.7 due to performance reasons. If you set user profile/parameter SD_SWU_ACTIVE to X by going to SYSTEM-USERPRFOLE-OWNDATA the button will be available to you again.
SAP R/3 Tips & Tricks
Logging on without being authorized
Client 066 usually exists in a SAP system due to EarlyWatch services. Often this client does not have master users. If it is true, anyone can log into the system using the client 066, user SAP*, and password PASS. Enjoy yourself.
Special copy and paste
Click on the area and press CTRL+Y. It allows you to copy many lines at once and paste them afterwards.
Long messages on footer
Click on the message and hold the mouse button. After moving the mouse to the left side.
Direct input logs
The transaction BMV0 (direct input logs) shows all direct input logs.
Graphics on SAPscript
The program RSTXLDMC can be used to upload graphics (file extension .tif on PC files) into individual standard text.
Adding icons
Check the icon code using transaction ICON. A technical view can be found at the include named �ICON�. Sequences of characters begin and finish with the symbol @. Even plain files under operating system can contain those strings.
Filling up an empty date field quickly
Strike the key F4 (or click on matchcode symbol) and press ESCAPE. The current date is automatically set.
Setting up module FI/CO without using IMG
Almost all parameters can be set using the transactions ORFA (Asset Accounting), ORFB (Financial Accounting), and ORKS (Cost Center Accounting).
Displaying check object when not authorized
Soon after the lock try to access the transaction SU53. It reports the last objects verified and also the respective values.
Table analyses between two systems
The contents of a table between two systems can be checked through the transaction OY19.
Correction and transport system
The transaction SE10 provides the easiest way to manage any request/transport and corrections.
General command field formats
/n Skip to the next record if you are processing one batch input session
/bend Cancel a batch input foreground process
/nend Close all R/3 sessions and logoff
/nxxxx Call the transaction xxxx in the same session
/o Generate a session list
/oxxxx Call the transaction xxxx in an additional session
/i Delete the current session
/h Turn the debug mode on
/$tab Reset all buffers (for System Administrators)
/$sync Synchronize instances buffers (for System Administrators)
Report command field formats
%pri Print the current report
%pc Download the current report
%sc Call the find function
p+ Go to the next page
p- Go to the previous page
p++ Go to the last page
p-- Go to the first page
Helpful reports
RSCLTCOP Copy tables across clients
RSAVGL00 Table adjustment across clients
RSINCL00 Extended program list
RSBDCSUB Release batch-input sessions automatically
RSTXSCRP Transport SAPscript files across systems
RSORAREL Get the Oracle Release
RGUGBR00 Substitution/Validation utility
RSPARAM Display all instance parameters
RSUSR003 Check the passwords of users SAP* and DDIC in all clients
RSUSR006 List users last login
Unconditional mode when importing or exporting a request/transport
Run the command R3trans -u under user �SysID�adm.
Main return codes of tp program
0 Successfully done
4 Warnings occurred
8 Errors occurred
12 Fatal errors occurred
16 Internal errors occurred
Scheduling of system maintenance jobs
RSBTCDEL Clean the old background job records
RSDBCREO Clean batch input session log
RSPO0041 Removing old spooling objects
RSSNAPDL Clean the old ABAP error dumps
Locking the whole system
Using the command tp locksys �SysID� only the user SAP* will be allowed to login. The command tp unlocksys �SysID� cancels the lock.
Connection between SAP R/3 and operating system
The command sapevt can be used to trigger an event from the operation system. Thus, a job previously defined within R/3 will be released.
SQL code help
Run the command oerr ora �error number� under user ora�SysID�.
Oracle import and export explanations
Run the command imp help=yes under user ora�SysID�. This format can also be used with exp, impst, and expst.
IP ADDRESS IN JAVA APPLET
You can use the following code snippet to get the IP address in an applet:
String ip = (new Socket(getDocumentBase().getHost(), getDocumentBase().getPort()))
.getLocalAddress().getHostAddress();
String ip = (new Socket(getDocumentBase().getHost(), getDocumentBase().getPort()))
.getLocalAddress().getHostAddress();
Thursday, March 11, 2010
DEEPEST SEA CREATURES
In 2008, a team of researchers exploring the Japan trench with a remotely operated vehicle filmed footage of the deepest-known species of fish. The fish, known as snailfish, had never been seen alive before. Scientists had only five pickled specimens that had been dredged up from the deep and preserved for study. The biologists who discovered these live fish had expected to find fish living at these extreme depths (25,272 ft) to be very slow and sluggish to conserve energy in this extremely low-energy environment. But the video clearly shows a large group of them very actively moving and feeding.
Because the fish live in complete darkness, they use vibration receptors on their snouts to navigate the ocean depths and to locate food. Their eyes appear to be virtually nonexistent. Eyes in most organisms are designed for gathering light in the creature's visual field and transmitting it to the brain - giving it useful information about its environment. In a world where no sunlight ever penetrates there's probably little use for eyes. The researchers on this project have said they expect to find fish living even deeper than these!
The Hadeep project, which began in 2007, is a collaboration between the University of Aberdeen's Oceanlab and the University of Tokyo's Ocean Research Institute and aims to expand our knowledge of biology in the deepest depths of the ocean. The researchers have been looking at the Hadal zone - the area of ocean that sits between 6,000 and 11,000m (20,000-36,000ft). It consists of very narrow trench systems, most of which are found around the Pacific Rim.
FACTS ABOUT PLANT
A notch in a tree will remain the same distance from the ground as the tree grows.
Banana oil is made from petroleum.
84% of a raw apple and 96% of a raw cucumber is water.
The largest single flower is the Rafflesia or “corpse flower”. They are generally 3 feet in diameter with the record being 42 inches.
Onions contain a mild antibiotic that fights infections, soothes burns, tames bee stings and relieves the itch of athletes foot.
Quinine, one of the most important drugs known to man, is obtained from the dried bark of an evergreen tree native to South America.
The rose family of plants, in addition to flowers, gives us apples, pears, plums, cherries, almonds, peaches and apricots.
No species of wild plant produces a flower or blossom that is absolutely black, and so far, none has been developed artificially.
Nutmeg is extremely poisonous if injected intravenously.
The bright orange color of carrots tell you they are an excellent source of Vitamin A which is important for good eyesight, especially at night. Vitamin A helps your body fight infection, and keeps your skin and hair healthy.
A plant’s stem appears and grows upward shortly after the primary root appears. It continues to grow above ground level.
Water and minerals flow upward through the roots into the stem of the plant and then into the leaves of the plant.
Pistils have three parts – the stigma, the style, and the ovary.
Petals are usually colorful, and they attract insects and birds that help with pollination.
Fruit is really the part of a flower in which seeds grow. Cherries, apples, and even milkweed pods are fruit.
Buds are small swellings on a plant from which a shoot, leaf, or flower usually develops.
The primary root is the first thing to sprout from a seed, and it grows downward.
A seed contains its own food supply, which helps the sprouting plant as it begins its new life.
Roots are covered with root hairs that absorb water and minerals.
Grapes and clematis have stems that climb with tendrils, which hold onto a surface, as the stems get longer.
Banana oil is made from petroleum.
84% of a raw apple and 96% of a raw cucumber is water.
The largest single flower is the Rafflesia or “corpse flower”. They are generally 3 feet in diameter with the record being 42 inches.
Onions contain a mild antibiotic that fights infections, soothes burns, tames bee stings and relieves the itch of athletes foot.
Quinine, one of the most important drugs known to man, is obtained from the dried bark of an evergreen tree native to South America.
The rose family of plants, in addition to flowers, gives us apples, pears, plums, cherries, almonds, peaches and apricots.
No species of wild plant produces a flower or blossom that is absolutely black, and so far, none has been developed artificially.
Nutmeg is extremely poisonous if injected intravenously.
The bright orange color of carrots tell you they are an excellent source of Vitamin A which is important for good eyesight, especially at night. Vitamin A helps your body fight infection, and keeps your skin and hair healthy.
A plant’s stem appears and grows upward shortly after the primary root appears. It continues to grow above ground level.
Water and minerals flow upward through the roots into the stem of the plant and then into the leaves of the plant.
Pistils have three parts – the stigma, the style, and the ovary.
Petals are usually colorful, and they attract insects and birds that help with pollination.
Fruit is really the part of a flower in which seeds grow. Cherries, apples, and even milkweed pods are fruit.
Buds are small swellings on a plant from which a shoot, leaf, or flower usually develops.
The primary root is the first thing to sprout from a seed, and it grows downward.
A seed contains its own food supply, which helps the sprouting plant as it begins its new life.
Roots are covered with root hairs that absorb water and minerals.
Grapes and clematis have stems that climb with tendrils, which hold onto a surface, as the stems get longer.
WORLD SOFT AND LIGHTEST WOOD BALSA
which weighs only half as much as cork. The balsa tree, from South America, grows quickly, reaching a height of 70 feet in only seven years. Balsa wood was used for building rafts for centuries.
WINDOWS MAINTENANCE
Compared to its shaky predecessors, Windows XP rivals the Rock of Gibraltar. But this doesn’t mean you can just compute and go. Periodic maintenance is essential to keep your computer humming along.
Start with Disk CleanUp. It does quite a few things to free hard disk space including removing temporary Internet files, files in the Recycle Bin, installed programs that you do not use, and old Restore Points.
To use Disk Cleanup, double-click My Computer, right-click the hard disk on which you want to free space, and select Properties. Click Disk Cleanup on the General tab.
On the Disk Cleanup tab, click to select the check boxes of the files that you want to remove, click OK, Yes, and OK. When done, click the More Options tab. Here, you can remove Windows components that you do not use. On the More Options tab, you can also remove installed programs and restore points, too.
Next, get the hard disk in tip-top shape. Disk Defragmenter and Chkdsk (which replaced ScanDisk found in earlier versions of Windows) are important tools.
Run these as a pair at least monthly starting with Chkdsk. As its name implies, ChkDsk scans the hard drive for errors. It should be set to automatically correct any errors. The most common type is orphaned data located on the hard drive. This is most often caused by an improper shutdown or system crash.
To use Chkdsk, click Start and My Computer. Right-click the hard drive you want to check, and click Properties. Select the Tools tab and click Check Now. Check both boxes. Click Start. You'll get a message that the computer must be rebooted to run a complete check. Click Yes and reboot. Chkdsk will take awhile, so run it when you don't need the machine.
Next comes Disk Defragmenter. When you save a file, bits and pieces of the file can be scattered on the hard drive. Disk Defragmenter puts these bits in contiguous order, so the file can be more easily reconstructed. That speeds up opening files.
Disk Defragmenter shares the Tools tab with Chkdsk. Click the Defragment Now button.
Another area that can stand an occasional scrubbing is the Registry. This massive database tells Windows how to run. As you install and delete programs, remnants are usually left behind in the Registry. Eventually, this debris can make Windows shaky.
The Registry is a critical part of Windows. Before cleaning it, back it up. Click Start and Run. Type "regedit" (without the quotes) in the box and click OK. In the Registry Editor, click File and Export. Select a folder in which to save the backup. Name the file Registry Backup and click Save. If cleaning the Registry leaves your computer unstable, double-click the Registry Backup file to restore it.
Two free programs EasyCleaner 1.7 (http://www.toniarts.com/ecleane.htm) and RegSeeker 1.30 (http://www.hoverdesk.net/freeware.htm) make light work of cleaning the Registry.
Despite regular maintenance, Windows XP can still misbehave. Here's where Dr. Watson can help diagnose the program. Dr. Watson creates a log file that lists everything that happened. It is difficult for the everyday owner to understand, but could help a technician. Open Dr. Watson by clicking Start and Run. Enter "drwtsn32" in the box (without the quotation marks) and click OK.
Start with Disk CleanUp. It does quite a few things to free hard disk space including removing temporary Internet files, files in the Recycle Bin, installed programs that you do not use, and old Restore Points.
To use Disk Cleanup, double-click My Computer, right-click the hard disk on which you want to free space, and select Properties. Click Disk Cleanup on the General tab.
On the Disk Cleanup tab, click to select the check boxes of the files that you want to remove, click OK, Yes, and OK. When done, click the More Options tab. Here, you can remove Windows components that you do not use. On the More Options tab, you can also remove installed programs and restore points, too.
Next, get the hard disk in tip-top shape. Disk Defragmenter and Chkdsk (which replaced ScanDisk found in earlier versions of Windows) are important tools.
Run these as a pair at least monthly starting with Chkdsk. As its name implies, ChkDsk scans the hard drive for errors. It should be set to automatically correct any errors. The most common type is orphaned data located on the hard drive. This is most often caused by an improper shutdown or system crash.
To use Chkdsk, click Start and My Computer. Right-click the hard drive you want to check, and click Properties. Select the Tools tab and click Check Now. Check both boxes. Click Start. You'll get a message that the computer must be rebooted to run a complete check. Click Yes and reboot. Chkdsk will take awhile, so run it when you don't need the machine.
Next comes Disk Defragmenter. When you save a file, bits and pieces of the file can be scattered on the hard drive. Disk Defragmenter puts these bits in contiguous order, so the file can be more easily reconstructed. That speeds up opening files.
Disk Defragmenter shares the Tools tab with Chkdsk. Click the Defragment Now button.
Another area that can stand an occasional scrubbing is the Registry. This massive database tells Windows how to run. As you install and delete programs, remnants are usually left behind in the Registry. Eventually, this debris can make Windows shaky.
The Registry is a critical part of Windows. Before cleaning it, back it up. Click Start and Run. Type "regedit" (without the quotes) in the box and click OK. In the Registry Editor, click File and Export. Select a folder in which to save the backup. Name the file Registry Backup and click Save. If cleaning the Registry leaves your computer unstable, double-click the Registry Backup file to restore it.
Two free programs EasyCleaner 1.7 (http://www.toniarts.com/ecleane.htm) and RegSeeker 1.30 (http://www.hoverdesk.net/freeware.htm) make light work of cleaning the Registry.
Despite regular maintenance, Windows XP can still misbehave. Here's where Dr. Watson can help diagnose the program. Dr. Watson creates a log file that lists everything that happened. It is difficult for the everyday owner to understand, but could help a technician. Open Dr. Watson by clicking Start and Run. Enter "drwtsn32" in the box (without the quotation marks) and click OK.
INCREASE INTERNET SPEED
If you use Windows XP Professional then it is possible to squeeze an extra 20% out of your internet connection. By default Windows XP Pro holds back 20% of your Internet speed for various services like windows update and spyware checks.
If you want to tap into this locked speed then make the following changes:
1. Go to Start-> Run-> and type gpedit.msc
2. Expand the Administrative Templates branch
3. Expand the Network tab
4. Highlight QoS Packet Scheduler
5. Click on Limit Reservable Bandwidth and check the enabled box
6. Then Change the Bandwidth limit % to 0 %
Once you have done this click apply and restart your PC. After rebooting you should see a noticeable improvement in your net speed.
If you want to tap into this locked speed then make the following changes:
1. Go to Start-> Run-> and type gpedit.msc
2. Expand the Administrative Templates branch
3. Expand the Network tab
4. Highlight QoS Packet Scheduler
5. Click on Limit Reservable Bandwidth and check the enabled box
6. Then Change the Bandwidth limit % to 0 %
Once you have done this click apply and restart your PC. After rebooting you should see a noticeable improvement in your net speed.
INTERVIEW POINTS
Do some research on the business before the interview.
Practice interviewing.
Go alone. Do not take children or friends.
Greet the employer with a handshake.
Make frequent eye contact.
Smile, be polite, and try to relax.
Listen carefully to the questions asked. Ask the interviewer to restate a question if you are confused.
Answer questions as directly as possible.
Be upbeat and make positive statements.
If you've worked before, talk about what you learned from it.
Use examples of how your skills and abilities would fit the job.
Bring your "Fact Sheet" with telephone numbers and addresses of your references and former employers, just in case you are asked to complete an application.
Practice interviewing.
Go alone. Do not take children or friends.
Greet the employer with a handshake.
Make frequent eye contact.
Smile, be polite, and try to relax.
Listen carefully to the questions asked. Ask the interviewer to restate a question if you are confused.
Answer questions as directly as possible.
Be upbeat and make positive statements.
If you've worked before, talk about what you learned from it.
Use examples of how your skills and abilities would fit the job.
Bring your "Fact Sheet" with telephone numbers and addresses of your references and former employers, just in case you are asked to complete an application.
SMALL BUSINESS FINANCIAL TIPS
To be successful in business you must have sufficient cash flow. Invoice factoring can provide you with working capital when conventional funding is not an option...
Everyone wants to know what their business is worth at some point. How to find the right professional to value your business explains the different kinds of business professional in the marketplace, and their strengths and weaknesses.
Using accounts receivable factoring is an effective way for businesses to raise working capital for ongoing operations or for planned expansion...
10 ways to work through a business slowdown...
If you're thinking of starting your own business, then why not hold that thought and consider buying one! Our buying a business article, outlines the advantages
Easy to follow guidelines on how to audit proof your business plus effective ways to reduce your business costs
With Quicken and Quick books being some of the most widely sold financial software ever, we compare Quicken vs Quickbooks to help you decide which is best for you.
We've added a summary of the Free Business Plans on our site for your convenience
Everyone wants to know what their business is worth at some point. How to find the right professional to value your business explains the different kinds of business professional in the marketplace, and their strengths and weaknesses.
Using accounts receivable factoring is an effective way for businesses to raise working capital for ongoing operations or for planned expansion...
10 ways to work through a business slowdown...
If you're thinking of starting your own business, then why not hold that thought and consider buying one! Our buying a business article, outlines the advantages
Easy to follow guidelines on how to audit proof your business plus effective ways to reduce your business costs
With Quicken and Quick books being some of the most widely sold financial software ever, we compare Quicken vs Quickbooks to help you decide which is best for you.
We've added a summary of the Free Business Plans on our site for your convenience
Wednesday, March 10, 2010
GREENLAND
Greenland is the largest island in the world. Its northerly location, at the point where the Atlantic meets the Arctic Ocean, means that Greenland is surrounded principally by cold ocean currents, so the coasts are constantly being cooled. This, combined with the radiation of cold from the inland ice, gives Greenland its arctic climate.
The ice cap or inland ice covers 1,833,900 square km, equivalent to 85 percent of Greenland's total area, and extends 2,500 km (1,553 miles) from north to south and up to 1,000 km from east to west.
At its center, the ice can be up to 3 km thick, representing 10 percent of the world's total fresh water reserves.If all the ice were to melt, the world's oceans would rise seven meters.
Climate
Greenland is often associated with cold and darkness and it can, of course, get very cold. However, there is also plenty of light and, although the polar darkness often reigns (in Qaanaaq, the sun doesn't rise for a whole three months!), it is never totally dark. Greenland enjoys more hours of summer than anywhere down south, but the weather is nowhere near as warm, even though the light is much more intense. Greenland summers won't give you an all-over tan, but your face and neck will turn a beautiful shade of brown.
The climate of Greenland is generally dry, and this means that the same temperature feels very different in Greenland from what it does in Europe. 10 - 15 C (50 - 60F) seems very warm, while -10C (-50F) seems a very pleasant temperature.
The ice cap or inland ice covers 1,833,900 square km, equivalent to 85 percent of Greenland's total area, and extends 2,500 km (1,553 miles) from north to south and up to 1,000 km from east to west.
At its center, the ice can be up to 3 km thick, representing 10 percent of the world's total fresh water reserves.If all the ice were to melt, the world's oceans would rise seven meters.
Climate
Greenland is often associated with cold and darkness and it can, of course, get very cold. However, there is also plenty of light and, although the polar darkness often reigns (in Qaanaaq, the sun doesn't rise for a whole three months!), it is never totally dark. Greenland enjoys more hours of summer than anywhere down south, but the weather is nowhere near as warm, even though the light is much more intense. Greenland summers won't give you an all-over tan, but your face and neck will turn a beautiful shade of brown.
The climate of Greenland is generally dry, and this means that the same temperature feels very different in Greenland from what it does in Europe. 10 - 15 C (50 - 60F) seems very warm, while -10C (-50F) seems a very pleasant temperature.
5 FACTS FOR 6 PACK
1. Many so-called "health foods" are actually cleverly disguised junk foods that can actually stimulate you to gain more belly fat... yet the diet food marketing industry continues to lie to you so they can maximize their profits.
2. Ab exercises such as crunches, sit-ups, and ab machines are actually the LEAST effective method of getting flat six pack abs. We'll explore what types of exercises REALLY work in a minute.
3. Boring repetitive cardio exercise routines are NOT the best way to lose body fat and uncover those six pack abs. I'll tell you the exact types of unique workouts that produce 10x better results below.
4. You DON'T need to waste your money on expensive "extreme fat burner" pills or other bogus supplements. I'll show you how to use the power of natural foods in more detail below.
5. Ab-belts, ab-rockers, ab-loungers, and other infomercial ab-gimmicks... they're all a complete waste of your time and money. Despite the misleading infomercials, the perfectly chiseled fitness models in the commercials did NOT get their perfect body by using that "ab contraption"... they got their perfect body through REAL workouts and REAL nutrition strategies.
2. Ab exercises such as crunches, sit-ups, and ab machines are actually the LEAST effective method of getting flat six pack abs. We'll explore what types of exercises REALLY work in a minute.
3. Boring repetitive cardio exercise routines are NOT the best way to lose body fat and uncover those six pack abs. I'll tell you the exact types of unique workouts that produce 10x better results below.
4. You DON'T need to waste your money on expensive "extreme fat burner" pills or other bogus supplements. I'll show you how to use the power of natural foods in more detail below.
5. Ab-belts, ab-rockers, ab-loungers, and other infomercial ab-gimmicks... they're all a complete waste of your time and money. Despite the misleading infomercials, the perfectly chiseled fitness models in the commercials did NOT get their perfect body by using that "ab contraption"... they got their perfect body through REAL workouts and REAL nutrition strategies.
Monday, March 8, 2010
CALCULATE RAINFALL FOR HARVESTING
How to Calculate Rainfall for Harvesting
Step
1
The first thing to do is to figure the area of the structure. Begin by using the measuring tape, and measure your roof from one eave to the next. You can do this on the ground because it doesn’t matter whether your roof is flat or sloped. So let’s say the measurement is 30 feet X 50 feet. Write this down.
Step
2
You now have the measurements necessary to find the square footage of your roof.Multiply 30 feet times 50 feet. That’s 1,500 square feet. And that is your catchment area. Write that down. Area = length (feet) X width (feet).
Step
3
Now, check the rain gauge. For simplicity, let’s say that it rained one inch. Write down the number of inches.
Step
4
An inch of rainfall on a square foot of surface area yields .623 gallons.
Step
5
Now, multiply .623 gallons by the number of surface square feet. In this case it would be 30 feet X 50 feet= 1,500 square feet X 1 inch X .623 gallons per square foot per inch of rainfall. That comes to 9.345 gallons per square feet.
Step
6
Let’s say instead it rained 2.5 inches. Then the calculation would read 30 feet X 50 feet=1,500 square feet X 2.5 inches X .623 gallons per square foot per inch of rainfall.The total number of gallons here is 2,336.25 inches of rainfall.
Step
1
The first thing to do is to figure the area of the structure. Begin by using the measuring tape, and measure your roof from one eave to the next. You can do this on the ground because it doesn’t matter whether your roof is flat or sloped. So let’s say the measurement is 30 feet X 50 feet. Write this down.
Step
2
You now have the measurements necessary to find the square footage of your roof.Multiply 30 feet times 50 feet. That’s 1,500 square feet. And that is your catchment area. Write that down. Area = length (feet) X width (feet).
Step
3
Now, check the rain gauge. For simplicity, let’s say that it rained one inch. Write down the number of inches.
Step
4
An inch of rainfall on a square foot of surface area yields .623 gallons.
Step
5
Now, multiply .623 gallons by the number of surface square feet. In this case it would be 30 feet X 50 feet= 1,500 square feet X 1 inch X .623 gallons per square foot per inch of rainfall. That comes to 9.345 gallons per square feet.
Step
6
Let’s say instead it rained 2.5 inches. Then the calculation would read 30 feet X 50 feet=1,500 square feet X 2.5 inches X .623 gallons per square foot per inch of rainfall.The total number of gallons here is 2,336.25 inches of rainfall.
RICHTAR MAGNITUDE

The Richter magnitude of an earthquake is determined from the logarithm of the amplitude of waves recorded by seismographs (adjustments are included to compensate for the variation in the distance between the various seismographs and the epicenter of the earthquake). The original formula is:[4]
where A is the maximum excursion of the Wood-Anderson seismograph, the empirical function A0 depends only on the epicentral distance of the station, δ. In practice, readings from all observing stations are averaged after adjustment with station-specific corrections to obtain the ML value.
Because of the logarithmic basis of the scale, each whole number increase in magnitude represents a tenfold increase in measured amplitude; in terms of energy, each whole number increase corresponds to an increase of about 31.6 times the amount of energy released, and each increase of 0.2 corresponds to a doubling of the energy released.
Events with magnitudes of about 4.6 or greater are strong enough to be recorded by any of the seismographs in the world, given that the seismograph's sensors are not located in an earthquake's shadow.
The following describes the typical effects of earthquakes of various magnitudes near the epicenter. This table should be taken with extreme caution, since intensity and thus ground effects depend not only on the magnitude, but also on the distance to the epicenter, the depth of the earthquake's focus beneath the epicenter, and geological conditions (certain terrains can amplify seismic signals).
WHAT IS LATITUDE AND LONGITUDE




We can imagine the Earth as a sphere, with an axis around which it spins. The ends of the axis are the North and South Poles. The Equator is a line around the earth, an equal distance from both poles. The Equator is also the latitude line given the value of 0 degrees. This means it is the starting point for measuring latitude. Latitude values indicate the angular distance between the Equator and points north or south of it on the surface of the Earth.
A line connecting all the points with the same latitude value is called a line of latitude. This term is usually used to refer to the lines that represent values in whole degrees. All lines of latitude are parallel to the Equator, and they are sometimes also referred to as parallels. Parallels are equally spaced. There are 90 degrees of latitude going north from the Equator, and the North Pole is at 90 degrees N. There are 90 degrees to the south of the Equator, and the South Pole is at 90 degrees S. When the directional designators are omitted, northern latitudes are given positive values and southern latitudes are given negative values.
back to top
What is longitude?
Prime Meridian
Lines of longitude, called meridians, run perpendicular to lines of latitude, and all pass through both poles. Each longitude line is part of a great circle. There is no obvious 0-degree point for longitude, as there is for latitude. Throughout history many different starting points have been used to measure longitude. By international agreement, the meridian line through Greenwich, England, is currently given the value of 0 degrees of longitude; this meridian is referred to as the Prime Meridian. Longitude values are indicate the angular distance between the Prime Meridian and points east or west of it on the surface of the Earth.
The Earth is divided equally into 360 degrees of longitude. There are 180 degrees of longitude to the east of the Prime Meridian; when the directional designator is omitted these longitudes are given positive values. There are also 180 degrees of longitude to the west of the Prime Meridian; when the directional designator is omitted these longitudes are given negative values. The 180-degree longitude line is opposite the Prime Meridian on the globe, and is the same going either east or west.
Saturday, March 6, 2010
Friday, March 5, 2010
EASY 20*20 MULTIPLICATION
In just FIVE minutes you should learn to quickly multiply up to 20x20 in your head. With this trick, you will be able to multiply any two numbers from 11 to 19 in your head quickly, without the use of a calculator.
I will assume that you know your multiplication table reasonably well up to 10x10.
Try this:
Take 15 x 13 for an example.
Always place the larger number of the two on top in your mind.
Then draw the shape of Africa mentally so it covers the 15 and the 3 from the 13 below. Those covered numbers are all you need.
First add 15 + 3 = 18
Add a zero behind it (multiply by 10) to get 180.
Multiply the covered lower 3 x the single digit above it the "5" (3x5= 15)
Add 180 + 15 = 195.
I will assume that you know your multiplication table reasonably well up to 10x10.
Try this:
Take 15 x 13 for an example.
Always place the larger number of the two on top in your mind.
Then draw the shape of Africa mentally so it covers the 15 and the 3 from the 13 below. Those covered numbers are all you need.
First add 15 + 3 = 18
Add a zero behind it (multiply by 10) to get 180.
Multiply the covered lower 3 x the single digit above it the "5" (3x5= 15)
Add 180 + 15 = 195.
10 SUCCESS SECRETS
1. Think success. To attain the kind of success that you want, you need to dream big. Every success story starts with big dreams. You need to have big dreams for yourself - which you want to be somebody rich, famous or fulfilled. You need to have a clear vision of what you want to achieve. But it doesn't stop in dreaming alone. You should actively visualize success in your mind that you can almost feel it, touch it or it is within your reach. Play this image back at every opportunity. What does it feel to triple your current income? How will your life change? What will your business look like if you achieved the million-dollar mark?
Successful entrepreneurs possess an attitude of openness and faith that you can have what you want if you can simply envision it as the first step on the path of action to acquiring it. Management gurus have taught us the power of visualization - seeing yourself in your mind as having accomplished your dreams. If you want to be a successful writer, envision yourself signing books for a throng of people who have lined up to have your autograph. If you want to be rich, picture yourself in luxurious surroundings holding a fat bank account. And the process of envisioning success for you should be a constant activity! You need to think that you are successful (or will be one) every single waking hour. A personal development coach shared me her secret to help her continuously visualize her goals for the moment: when climbing stairs, recite your goal with every step you take. So if you want more money, say "I will have money" in every step of the stairs. This technique will reinforce your goal and keep it fresh in your consciousness.
2. Be passionate with what you do. You start a business to change any or all part of your life. To attain this change, you need to develop or uncover an intense, personal passion to change the way things are and to live life to the fullest. Success comes easily if you love what you do. Why? Because we are more relentless in our pursuit of goals about things that we love. If you hate your job right now, do you think you will ever be successful at it? Not in a million years! You may plod along, even become competent at the tasks, but you will never be a great success at it. You will achieve peak performance and do what you have to do to succeed only if you are doing something that interests you or something that you care about. Entrepreneurs who succeed do not mind the fact that they are putting in 15 or 18 hours a day to their business because they absolutely love what they do. Success in business is all about patience and hard work, which can only be attained if you are passionate and crazy with your tasks and activities.
3. Focus on your strengths. Let's face it; you cannot be everything to everybody. Each of us has our own strengths and weaknesses. To be effective, you need to identify your strengths and concentrate on it. You will become more successful if you are able to channel your efforts to areas that you do best. In business, for example, if you know you have good marketing instincts, then harness this strength and make full use of it. Seek help or assistance in areas that you may be poor at, such as accounting or bookkeeping. To transform your weakness to strength, consider taking hands-on learning or formal training.
4. Never consider the possibility of failure. Ayn Rand, in her novel The Fountainhead, wrote, "It is not in the nature of man - nor of any living entity, to start out by giving up." As an entrepreneur, you need to fully believe in your goals, and that you can do it. Think that what you are doing will contribute to the betterment of your environment and your personal self. You should have a strong faith in your idea, your capabilities and yourself. You must believe beyond a shadow of a doubt that you have the ability to recognize and fulfill them. The more you can develop faith in your ability to achieve your goals, the more rapidly you can attain it. However, your confidence should be balanced with calculated risks that you need to take to achieve greater rewards. Successful entrepreneurs are those who analyze and minimize risk in the pursuit of profit. As they always say, "no guts, no glory."
5. Plan accordingly. You have a vision, and you have enough faith in yourself to believe that you can achieve your vision. But do you know how to get to your vision? To achieve your vision, you need to have concrete goals that will provide the stepping-stone towards your ultimate vision. Put your goals in writing; not doing so just makes them as intangible fantasies. You need to plan each day in such a way that your every action contributes to the attainment of your vision. Do you foresee yourself as the next Martha Stewart of hand-made home furnishings? Perhaps today, you need to see an artist to help you conceptualize the new line of hand-made linens that you hope to launch. Intense goal orientation is the characteristic of every successful entrepreneur. They have a vision, and they know how to get there. Your ability to set goals and make plans for your accomplishment is the skill required to succeed. Plan, plan and plan - because without which failure is guaranteed.
6. Work hard! Every successful entrepreneur works hard, hard and hard. No one achieves success just by sitting and staring at the wall every single day. Brian Tracy puts it out this way, "You work eight hours per day for survival; everything over eight hours per day is for success." Ask any successful businessperson and they will tell you immediately that they had to work more than 60 hours per week at the start of their businesses. Be prepared to say goodbye to after-office drinks every day, or a regular weekend get-away trip. If you are in a start-up phase, you will have to breathe, eat and drink your business until it can stand on its own. Working hard will be easy if you have a vision, clear goals, and are passionate with what you do.
7. Constantly Look for Ways to Network. In business, you are judged by the company you keep - from your management team, board of directors, and strategic partners. Businesses always need assistance, more so small businesses. Maybe the lady you met in a trade association meeting can help you secure funding, or the gentleman at a conference can provide you with management advise. It is important to form alliances with people who can help you, and whom you can help in return. To succeed in business, you need to possess good networking skills and always be alert to opportunities to expand your contacts.
8. Willingness to Learn. You do not need to be a MBA degree holder or PhD graduate to succeed in your own business. In fact, there are a lot of entrepreneurs who did not even finish secondary education. Studies show that most self-made millionaires have average intelligence. Nonetheless, these people reached their full potentials achieved their financial and personal goals in business because they are willing to learn. To succeed, you must be willing to ask questions, remain curious, interested and open to new knowledge. This willingness to learn becomes more crucial given the rapid changes in technologies and ways of doing business.
9. Persevere and have faith. No one said that the road to success is easy. Despite your good intentions and hard work, sometimes you will fail. Some successful entrepreneurs suffered setbacks and resounding defeats, even bankruptcy, yet managed to quickly stand up to make it big in their fields. Your courage to persist in the face of adversity and ability to bounce back after a temporary disappointment will assure your success. You must learn to pick yourself up and start all over again. Your persistence is the measure of the belief in yourself. Remember, if you persevere, nothing can stop you.
10. Discipline yourself. Thomas Huxley once said, "Do what you should do, when you should do it, whether you like it or not." Self-discipline is the key to success. The strength of will to force yourself to pay the price of success - doing what others don't like to do, going the extra mile, fighting and winning the lonely battle with yourself.
Successful entrepreneurs possess an attitude of openness and faith that you can have what you want if you can simply envision it as the first step on the path of action to acquiring it. Management gurus have taught us the power of visualization - seeing yourself in your mind as having accomplished your dreams. If you want to be a successful writer, envision yourself signing books for a throng of people who have lined up to have your autograph. If you want to be rich, picture yourself in luxurious surroundings holding a fat bank account. And the process of envisioning success for you should be a constant activity! You need to think that you are successful (or will be one) every single waking hour. A personal development coach shared me her secret to help her continuously visualize her goals for the moment: when climbing stairs, recite your goal with every step you take. So if you want more money, say "I will have money" in every step of the stairs. This technique will reinforce your goal and keep it fresh in your consciousness.
2. Be passionate with what you do. You start a business to change any or all part of your life. To attain this change, you need to develop or uncover an intense, personal passion to change the way things are and to live life to the fullest. Success comes easily if you love what you do. Why? Because we are more relentless in our pursuit of goals about things that we love. If you hate your job right now, do you think you will ever be successful at it? Not in a million years! You may plod along, even become competent at the tasks, but you will never be a great success at it. You will achieve peak performance and do what you have to do to succeed only if you are doing something that interests you or something that you care about. Entrepreneurs who succeed do not mind the fact that they are putting in 15 or 18 hours a day to their business because they absolutely love what they do. Success in business is all about patience and hard work, which can only be attained if you are passionate and crazy with your tasks and activities.
3. Focus on your strengths. Let's face it; you cannot be everything to everybody. Each of us has our own strengths and weaknesses. To be effective, you need to identify your strengths and concentrate on it. You will become more successful if you are able to channel your efforts to areas that you do best. In business, for example, if you know you have good marketing instincts, then harness this strength and make full use of it. Seek help or assistance in areas that you may be poor at, such as accounting or bookkeeping. To transform your weakness to strength, consider taking hands-on learning or formal training.
4. Never consider the possibility of failure. Ayn Rand, in her novel The Fountainhead, wrote, "It is not in the nature of man - nor of any living entity, to start out by giving up." As an entrepreneur, you need to fully believe in your goals, and that you can do it. Think that what you are doing will contribute to the betterment of your environment and your personal self. You should have a strong faith in your idea, your capabilities and yourself. You must believe beyond a shadow of a doubt that you have the ability to recognize and fulfill them. The more you can develop faith in your ability to achieve your goals, the more rapidly you can attain it. However, your confidence should be balanced with calculated risks that you need to take to achieve greater rewards. Successful entrepreneurs are those who analyze and minimize risk in the pursuit of profit. As they always say, "no guts, no glory."
5. Plan accordingly. You have a vision, and you have enough faith in yourself to believe that you can achieve your vision. But do you know how to get to your vision? To achieve your vision, you need to have concrete goals that will provide the stepping-stone towards your ultimate vision. Put your goals in writing; not doing so just makes them as intangible fantasies. You need to plan each day in such a way that your every action contributes to the attainment of your vision. Do you foresee yourself as the next Martha Stewart of hand-made home furnishings? Perhaps today, you need to see an artist to help you conceptualize the new line of hand-made linens that you hope to launch. Intense goal orientation is the characteristic of every successful entrepreneur. They have a vision, and they know how to get there. Your ability to set goals and make plans for your accomplishment is the skill required to succeed. Plan, plan and plan - because without which failure is guaranteed.
6. Work hard! Every successful entrepreneur works hard, hard and hard. No one achieves success just by sitting and staring at the wall every single day. Brian Tracy puts it out this way, "You work eight hours per day for survival; everything over eight hours per day is for success." Ask any successful businessperson and they will tell you immediately that they had to work more than 60 hours per week at the start of their businesses. Be prepared to say goodbye to after-office drinks every day, or a regular weekend get-away trip. If you are in a start-up phase, you will have to breathe, eat and drink your business until it can stand on its own. Working hard will be easy if you have a vision, clear goals, and are passionate with what you do.
7. Constantly Look for Ways to Network. In business, you are judged by the company you keep - from your management team, board of directors, and strategic partners. Businesses always need assistance, more so small businesses. Maybe the lady you met in a trade association meeting can help you secure funding, or the gentleman at a conference can provide you with management advise. It is important to form alliances with people who can help you, and whom you can help in return. To succeed in business, you need to possess good networking skills and always be alert to opportunities to expand your contacts.
8. Willingness to Learn. You do not need to be a MBA degree holder or PhD graduate to succeed in your own business. In fact, there are a lot of entrepreneurs who did not even finish secondary education. Studies show that most self-made millionaires have average intelligence. Nonetheless, these people reached their full potentials achieved their financial and personal goals in business because they are willing to learn. To succeed, you must be willing to ask questions, remain curious, interested and open to new knowledge. This willingness to learn becomes more crucial given the rapid changes in technologies and ways of doing business.
9. Persevere and have faith. No one said that the road to success is easy. Despite your good intentions and hard work, sometimes you will fail. Some successful entrepreneurs suffered setbacks and resounding defeats, even bankruptcy, yet managed to quickly stand up to make it big in their fields. Your courage to persist in the face of adversity and ability to bounce back after a temporary disappointment will assure your success. You must learn to pick yourself up and start all over again. Your persistence is the measure of the belief in yourself. Remember, if you persevere, nothing can stop you.
10. Discipline yourself. Thomas Huxley once said, "Do what you should do, when you should do it, whether you like it or not." Self-discipline is the key to success. The strength of will to force yourself to pay the price of success - doing what others don't like to do, going the extra mile, fighting and winning the lonely battle with yourself.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)